
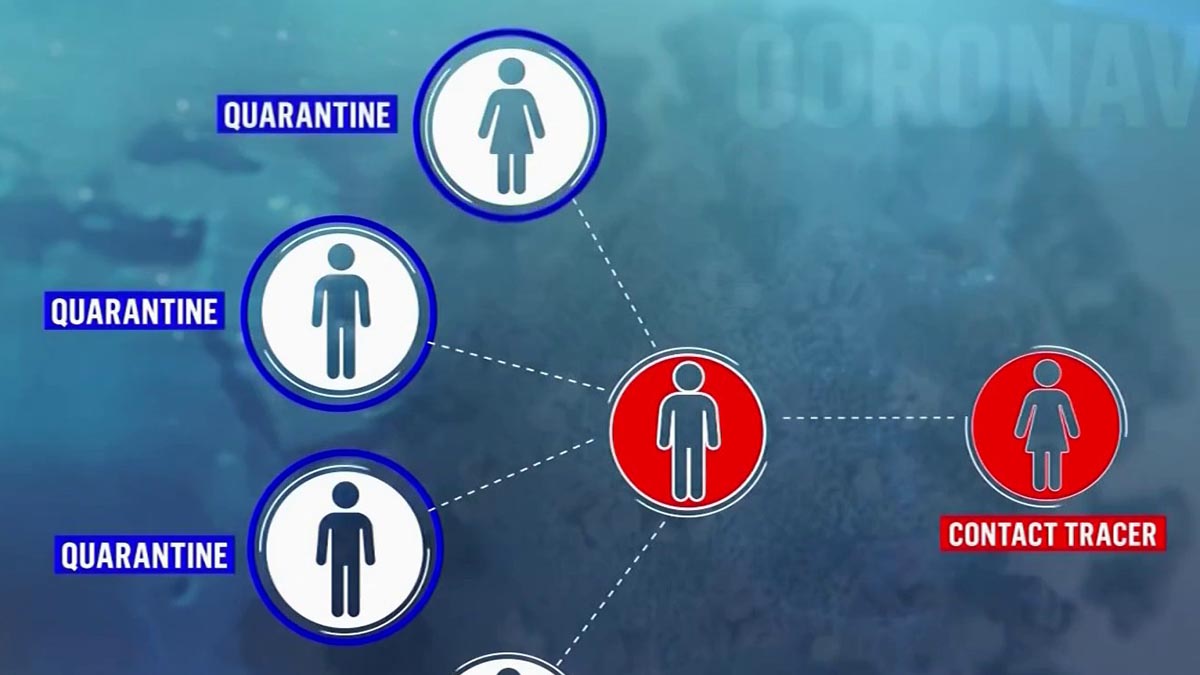
The index, sibling and child cases all spread their infection further. On the left, a transmission chain is shown where COVID-19 spreads from a parent case to an index case and their sibling case at a shared source event.
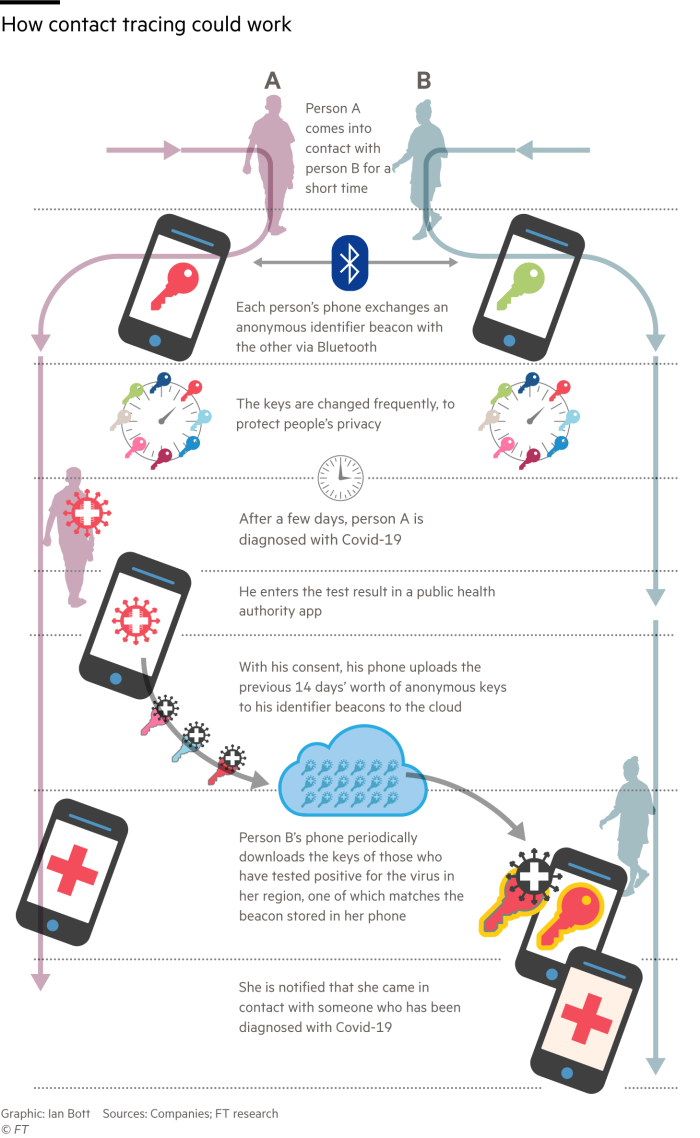
Forward contact tracing is the focus in most jurisdictions and has shown its ability to decrease COVID-19 transmission (Fig. In addition to child cases, any practical forward tracing strategy probably identifies the parent case (the infector of the index case) and sibling cases (infected by the same parent case) some of the time, for example if the index case had repeated contact with their parent or sibling case during their own infectious period, or if the time from the index case’s infection to their symptom onset or diagnosis was less than 2 days 12. In the light of substantial asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmission, the infectious period is generally assumed to start 2 days prior to onset of symptoms or diagnosis, whichever came first 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18. Worldwide investments in contact tracing programmes and research on the topic have not prevented repeated resurgence of community transmission of COVID-19, underscoring the urgent need for improved knowledge on the effective implementation of this key public health measure 6, 9.įorward contact tracing of an index case (the person diagnosed with COVID-19 undergoing contact tracing) intends to interrupt onward transmission from child cases (persons infected by the index case) by quarantining and/or testing contacts the index case has encountered during their infectious period 10, 11, 12.
It has been a staple public health intervention in a variety of infectious diseases, notably sexually transmitted diseases and tuberculosis 7, 8.

More infections are prevented, and epidemic control is improved, if the identification of patients and contacts at risk is rapid and comprehensive 3, 4, 5, 6. Case-based interventions such as case isolation or contact tracing with quarantine have been crucial in controlling the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, while reducing the need for indiscriminate contact reductions with high economic cost 1, 2.Ĭontact tracing aims to identify and interrupt transmission chains by isolating infected patients and quarantining those at risk from infection.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
